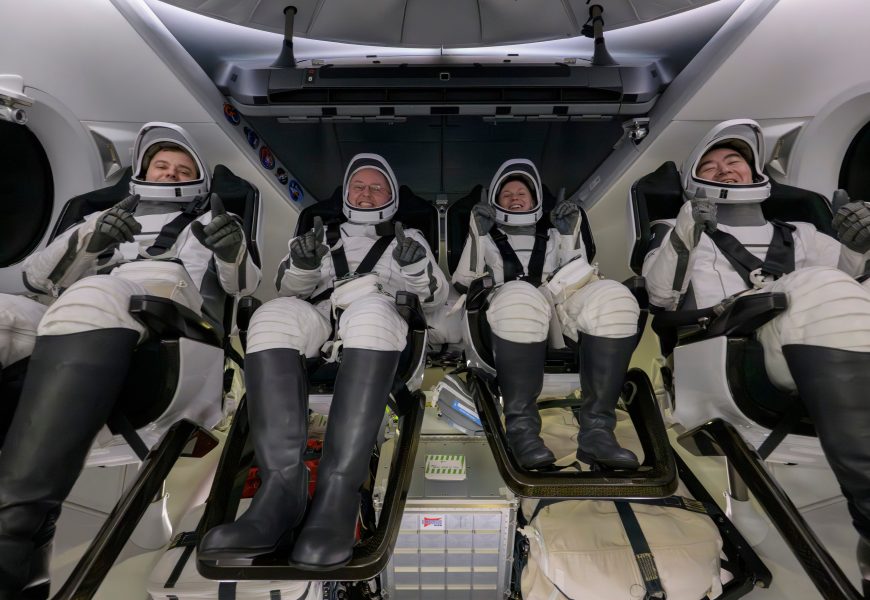
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) – An ailing astronaut returned to Earth with three others on Thursday, ending their space station mission more than a month early in NASA’s first medical evacuation.
Ailing astronaut returns to Earth early in NASA’s first medical evacuation
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) - An ailing astronaut returned to Earth with three others on Thursday, ending their space station mission more than a month early in NASA's first medical evacuation.
SpaceX guided the capsule to a middle-of-the-night splashdown in the Pacific near San Diego, less than 11 hours after the astronauts exited the International Space Station. Their first stop was a hospital for an overnight stay.
"Obviously, we took this action (early return) because it was a serious medical condition," NASA's new administrator Jared Isaacman said following splashdown. "The astronaut in question is fine right now, in good spirits and going through the proper medical checks."
It was an unexpected finish to a mission that began in August and left the orbiting lab with only one American and two Russians on board. NASA and SpaceX said they would try to move up the launch of a fresh crew of four; liftoff is currently targeted for mid-February.
NASA's Zena Cardman and Mike Fincke were joined on the return by Japan's Kimiya Yui and Russia's Oleg Platonov. Officials have refused to identify the astronaut who developed the health problem last week or explain what happened, citing medical privacy.
While the astronaut was stable in orbit, NASA wanted them back on Earth as soon as possible to receive proper care and diagnostic testing. The entry and splashdown required no special changes or accommodations, officials said, and the recovery ship had its usual allotment of medical experts on board.
The astronauts emerged from the capsule, one by one, within an hour of splashdown. They were helped onto reclining cots and then whisked away for standard medical checks, waving to the cameras. Isaacman monitored the action from Mission Control in Houston, along with the crew's families.
NASA decided a few days ago to take the entire crew straight to a San Diego-area hospital following splashdown and even practiced helicopter runs there from the recovery ship. The astronaut in question will receive in-depth medical checks before flying with the rest of the crew back to Houston on Friday, assuming everyone is well enough. Platonov's return to Moscow was unclear.
NASA stressed repeatedly over the past week that this was not an emergency. The astronaut fell sick or was injured on Jan. 7, prompting NASA to call off the next day's spacewalk by Cardman and Fincke, and ultimately resulting in the early return. It was the first time NASA cut short a spaceflight for medical reasons. The Russians had done so decades ago.
Spacewalk preparations did not lead to the medical situation, Isaacman noted, but for anything else, "it would be very premature to draw any conclusions or close any doors at this point." It's unknown whether the same thing could have happened on Earth, he added.
The space station has gotten by with three astronauts before, sometimes even with just two. NASA said it will be unable to perform a spacewalk, even for an emergency, until the arrival of the next crew, which has two Americans, one French and one Russian astronaut.
Isaacman said it's too soon to know whether the launch of station reinforcements will take priority over the agency's first moonshot with astronauts in more than a half-century. The moon rocket moves to the pad this weekend at Florida's Kennedy Space Center, with a fueling test to be conducted by early next month. Until all that is completed, a launch date cannot be confirmed; the earliest the moon flyaround could take off is Feb. 6.
For now, NASA is working in parallel on both missions, with limited overlap of personnel, according to Isaacman.
"If it comes down to a point in time to where we have to deconflict between two human spaceflight missions, that is a very good problem to have at NASA," he told reporters.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Department of Science Education and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.